Biofuels
2021 JUL 14
Preliminary >
Science and Technology > Energy > Biofuels
Why in news?
- Minister for Road Transport and Highways Nitin Gadkari said more use of alternate fuels including biofuels would bring respite from surging petrol prices that are now “agitating” people.
What are Biofuels?
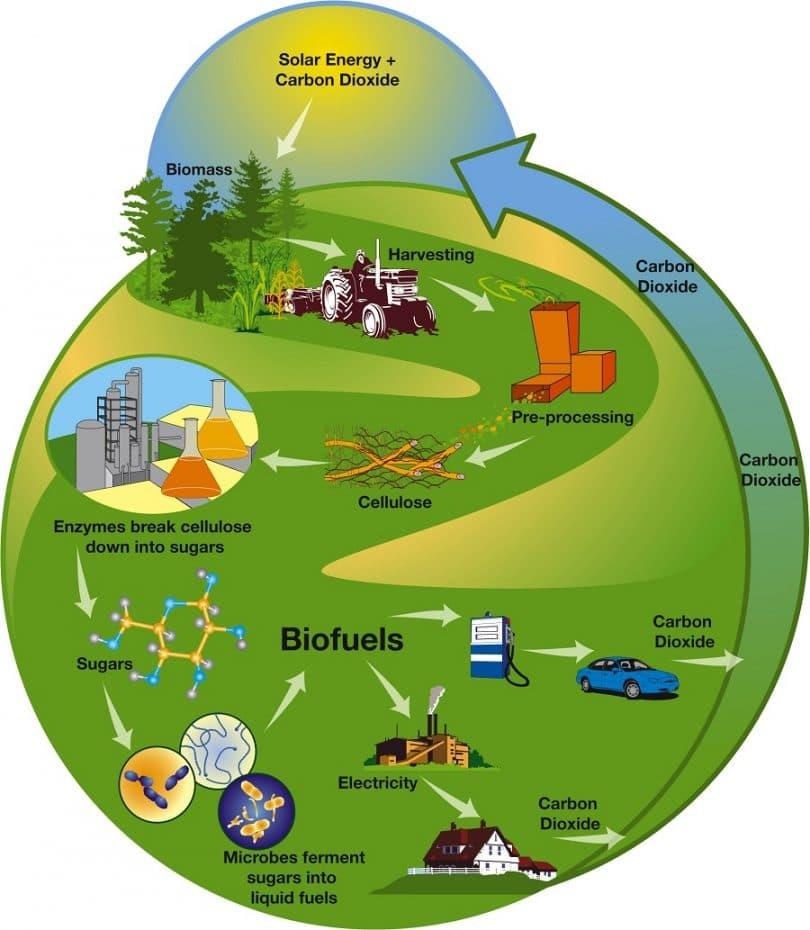
- Biofuels are combustible fuels created from biomass; in other words, fuels created from recently living plant matter as opposed to ancient plant matter in hydrocarbons.
Types of biofuels:
- Biogas - produced by the process of anaerobic digestion of organic material by anaerobic bacteria.
- Ethanol - produced by the action of microorganisms and enzymes through the fermentation of sugars or starches.
- Biodiesel - produced from oils or fats using transesterification.
First-generation biofuels:
- First-generation" or conventional biofuels are biofuels made from food crops grown on arable land. They are made from sugar, starch, or vegetable oil.
- Their feedstock (the plant or algal material from which they are generated) is not sustainable/green or, if used in large quantity, would have a large impact on the food supply.
Second-generation biofuels:
- Second-generation biofuels, also known as advanced biofuels, are fuels that can be manufactured from various types of non-food biomass.
- They include lignocellulosic biomass or woody crops, agricultural residues or waste, as well as dedicated non-food energy crops grown on marginal land unsuitable for crop production.
- They are “greener” in that they are made from sustainable feedstock – with lesser greenhouse gas emissions, and lesser impact on biodiversity and land use (water, food supply, etc.).
Third-generation biofuels:
- Third Generation of biofuels is based on improvements in the production of biomass.
- It takes advantage of specially engineered energy crops such as algae as its energy source.
Fourth-generation biofuels:
- Fourth generation biofuels couple carbon capture and storage along with the benefits of third generation fuels.
- However, unlike third-generation biofuels, they do not require the destruction of biomass.
- This class of biofuels includes technologies such as electrofuels and photobiological solar fuels.
PRELIMS QUESTION
Consider the following:
1.Reducing import dependency
2.Cleaner environment
3.Additional income to farmers
Which of these are the expected benefits of using Biofuels?
(a)1 only
(b)2 only
(c)1 and 2 only
(d)1, 2 and 3
Answer to prelims question
