End-to-End Encryption
2022 DEC 29
Mains >
Science and Technology > IT & Computers > Communication technology
IN NEWS:
- Recently, Apple announced that it will introduce end-to-end encryption for most of the data on iCloud by early 2023.
- Apple also said that users who opt in for end-to-end encryption on their iCloud will have a vast majority of their data protected even in case of a data breach in the cloud.
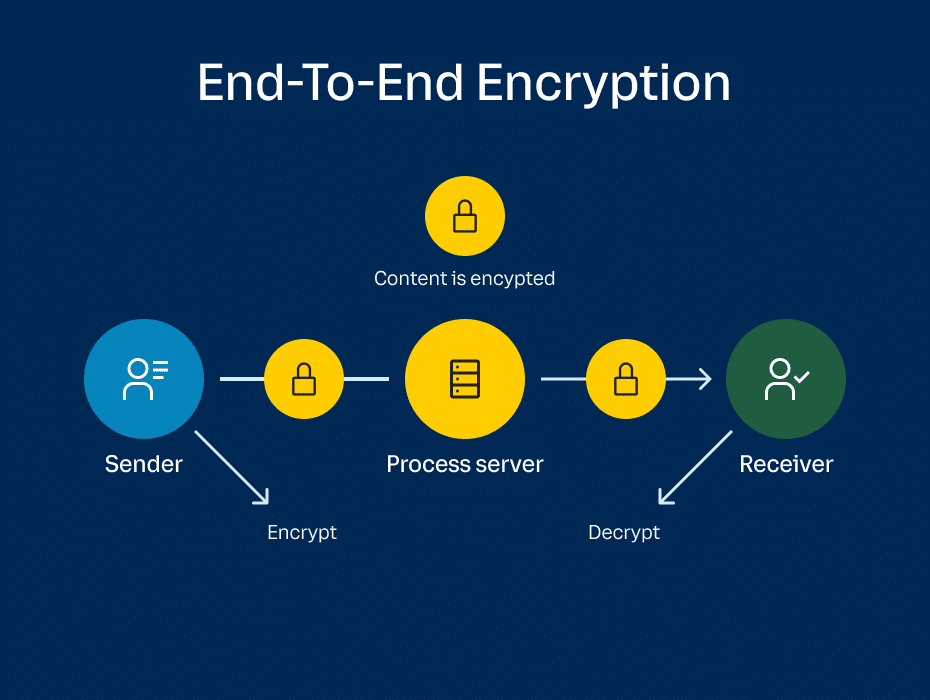
WHAT IS END-TO-END ENCRYPTION?
- End-to-end encryption (E2EE) is a method of secure communication that prevents third parties from accessing data while it's transferred from one end system or device to another.
- In E2EE, the data is encrypted on the sender's system or device, and only the intended recipient can decrypt it.
- As it travels to its destination, the message cannot be read or tampered with by an internet service provider (ISP), application service provider, hacker or any other entity or service.
- The process of end-to-end encryption uses an algorithm that transforms standard text into an unreadable format.
- This format can only be unscrambled and read by those with the decryption keys, which are only stored on endpoints and not with any third parties including companies providing the service.
- Some of the popular instant-messaging apps that use end-to-end encryption are Signal, WhatsApp, iMessage, and Google Messages.
- End-to-end encryption is also used to secure passwords, protect stored data, and safeguard data on cloud storage.
------------------------------
ADVANTAGES OF END-TO-END ENCRYPTION:
- Enhanced data security:
- End-to-end encryption uses public key cryptography, which stores private keys on the endpoint devices.
- Messages or data can only be decrypted using these keys, so only people with access to the endpoint devices are able to read the message.
|
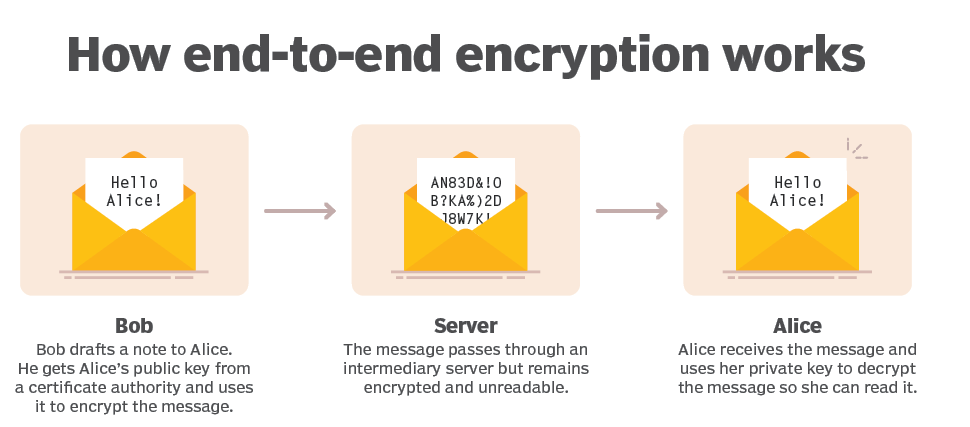
Public key cryptography:
- Public key cryptography is a method of encrypting or signing data with two different keys and making one of the keys, the public key, available for anyone to use. The other key is known as the private key.
- Data encrypted with the public key can only be decrypted with the private key.
- Because of this use of two keys instead of one, public key cryptography is also known as asymmetric cryptography.
|
- Improves Data Integrity (Tamper Proof):
- Without end-to-end encryption, the possibility exists of unauthorized users tampering with data while it’s in transit.
- In end-to-end encryption, the decryption key does not have to be transmitted; the recipient will already have it.
- If a message encrypted with a public key gets altered or tampered with in transit, the recipient will not be able to decrypt it, so the tampered contents will not be viewable.
- Highly Sensitive Data Exchanges:
- In case of highly sensitive data exchanges like the sharing of sensitive government intelligence data, end-to-end encryption is one solution that makes sure that no one outside of the sending and receiving parties can spread highly sensitive information.
- The reasons are twofold: 1) The key system in end-to-end encryption prevents unauthorized devices from opening the message. 2) If users maliciously or accidentally come across the message, end-to-end encryption has made it indecipherable to them.
- Device-level encryption:
- Other types of encryption focus on encrypting data at the server level, but if a malicious actor or other outsider gains access to that server, they can decrypt any information in that server fairly easily.
- Overcoming end-to-end encryption requires hackers to perform device-level hacks to get the information that they want, which is considerably more difficult and time-consuming to do, leading most hackers to avoid those types of attacks altogether.
- Compliance:
- Many industries are bound by regulatory compliance laws that require encryption-level data security. End-to-end encryption can help organizations protect that data by making it unreadable.
DISADVANTAGES OF END-TO-END ENCRYPTION:
- Unreliable receiving devices:
- End-to-end encryption does not guarantee the protection of data once it reaches the receiving device.
- If there’s a security problem on that device or if that device falls into the wrong hands, the data has already been decrypted on the receiving device, leaving it susceptible to outside parties who gain access to the device.
- Law enforcement and surveillance concerns:
- One of the most important and highly controversial issues with end-to-end encryption is that it’s almost too successful at protecting data from third parties.
- With this level of encryption, law enforcement and intelligence agencies cannot access evidence that has been encrypted, and neither can service providers if they are asked to cooperate in the investigation.
- In serious cases related to allegations like terrorism, murder, and physical abuse, this data protection becomes a major hindrance to public safety and national security.
- For instance, the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) said in a statement that end-to-end encryption and user-only access hinder its ability to protect people from cyber-attacks, violence against children, and terrorism.
- Visible metadata:
- Although messages in transit are encrypted and impossible to read, information about the message, such as the date it was sent and the recipient, is still visible, which may provide useful information to an interloper.
- Not future-proof:
- Although end-to-end encryption is a strong technology now, there is speculation that eventually quantum computing will render cryptography obsolete.
INDIA’S STANCE ON ENCRYPTION:
- Though India has 53 crore people using WhatsApp, 41 crore people using Facebook, and 21 crore people using Instagram, as per the Government of India (GoI) data, India does not have an all-encompassing legal framework for encryption. But there are certain sector-specific encryption mandates that have been given by regulators like the RBI, SEBI, etc.
- Draft National Policy on Encryption:
- In 2015, the Government tried to bring a draft National Policy on Encryption which had to be withdrawn within two days after concerns were raised by stakeholders about its provisions being vague and ambiguous.
- Personal Data Protection (PDP) Bill, 2019:
- In 2019, the Personal Data Protection (PDP) Bill brought by the Government mentioned the use of encryption and de-identification between data fiduciaries (companies) and data principals (users) as a security safeguard mechanism in Section 24 (1) (a).(The government withdrew the PDP Bill and recently released the Digital Personal Data Protection Bill, 2022 https://ilearncana.com/details/Digital-Personal-Data-Protection-Bill-2022/3760)
- The Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules 2021:
- The new IT rules brought in by the GoI, mandate social media intermediaries to provide for identification of users who originated any instigatory message. This is problematic because this provision could potentially disband the existing end-to-end encryption model and infringe upon the privacy of individuals.
CONCLUSION:
- Breaking the end-to-end encryption setup would introduce a whole new set of privacy concerns, with a huge potential for individual user privacy violations and illegal surveillance of users' chats by state machineries. Also, diluting encryption does not necessarily stop the proliferation of instigatory material; it simply leads to the proliferation of illegal encryption products or even communication via the Dark Web. Hence, the need of the hour is to have a well-defined law, passed by Parliament after due deliberations, governing the entire framework of encryption.
PRACTICE QUESTION:
Q. “One of the most important and highly controversial issues with end-to-end encryption is that it’s almost too successful at protecting data from third parties”. Discuss the statement with reference to the advantages and challenges associated with end-to-end encryption.
