India Vietnam Relations
2022 JUL 3
Mains >
International relations > India and Global Regions > India & South East Asia
IN NEWS:
- India and Vietnam signed a “Joint Vision” document to “significantly enhance the scope and scale” of bilateral ties by 2030 during the recent Vietnam visit of Indian Defence Minister Rajnath Singh.
HISTORY:
- India and Vietnam, with historical roots in the common struggle for liberation from colonial rule and the national struggle for independence, share traditionally close and cordial bilateral relations.
- India was the Chairman of the International Commission for Supervision and Control (ICSC), which was formed pursuant to the Geneva Accord of 1954 to facilitate the peace process in Vietnam.
- India initially maintained Consulate-level relations with the then North and South Vietnams and later established full diplomatic relations with unified Vietnam
- The relations between the two countries were elevated to the level of “Strategic Partnership” in 2007. The relations were further upgraded to “Comprehensive Strategic Partnership” in 2016.
SIGNIFICANCE OF VIETNAM FOR INDIA:
- Economic interests:
- Both the countries are among the fastest-growing economies of Asia. Also, they have a broad convergence of interest with respect to creating alternative supply chains in Asia against the China-centric supply chain.
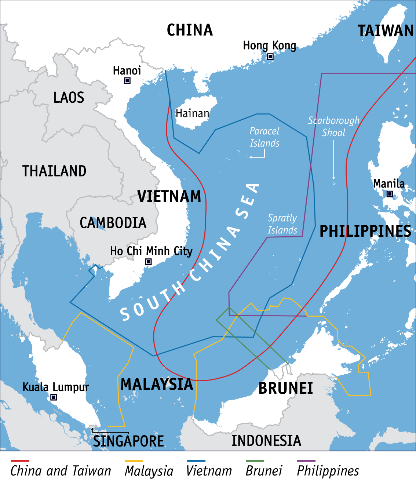
- Countering Chinese aggressions:
- The two countries are equally concerned about the aggressive and expansionist policies of China in the Indo-Pacific region. Vietnam was among the leading ASEAN countries to openly call out China for its aggressive stance in the disputed South China Sea.
- Strategic interests:
- Vietnam is crucial in ensuring peace and stability in the Indo-Pacific. This is why Vietnam was made part of the “Quad Plus” group of seven countries.
- India also has strategic investments, such as ONGC Videsh Ltd (OVL)’s oil exploration project in Block 128 (which is within Vietnam’s Exclusive economic zone) in the South China Sea.
- Defence exports:
- Through measures like the Comprehensive Strategic Partnership, India provides necessary assistance in developing Vietnam’s defence capabilities. This also helps India to export its defence capabilities.
- Eg: During the recent visit, India handed over 12 high-speed guard boats to Vietnam: Five of those were built in India, and the rest in a Vietnamese shipyard under India’s USD 100 million Defence Line of Credit.
- Success of Act East policy:
- Vietnam serves as an important partner in India’s “Act East” Policy and in enhancing ties with the other ASEAN countries.
- Cooperation in regional forums:
- India and Vietnam closely cooperate in various regional forums such as ASEAN, East Asia Summit, Mekong Ganga Cooperation, Asia Europe Meeting (ASEM) besides UN and WTO.
AREAS OF COOPERATION:
- Political exchanges:
- Regular high-level visits have happened between the two nations. Eg: Indian Defence Minister Rajnath Singh paid a three-day visit in June 2022 to Hanoi to strengthen defence and security ties with Vietnam.
- There are several bilateral mechanisms at different levels between India and Vietnam. Eg: Joint Commission Meeting at the Foreign Ministers' level and the Foreign Office Consultations and Strategic Dialogue at Secretary-level.
- Trade and economic cooperation:
- In FY 2020-21, for India, Vietnam was the 15th largest trading partner globally and the 4th largest within ASEAN. For Vietnam, on the other hand, India was the 10th largest trading partner globally.
- As of 2020, India’s investments in Vietnam are estimated at around USD 1.9 billion in total, whereas Vietnam has six investment projects in India with total estimated investment of USD 28.55 million.
- Development partnerships:
- India has been providing assistance to Vietnam within the ASEAN framework. Under the Mekong Ganga Cooperation (MGC) framework, India has been taking up Quick Impact Projects (QIPs), each valued at US$ 50,000, in different provinces of Vietnam for development of community infrastructure.
|
Mekong Ganga Cooperation (MGC):
- The MGC is an initiative by six countries – India and five ASEAN countries, namely, Cambodia, Lao PDR, Myanmar, Thailand and Vietnam launched in 2000 for cooperation in tourism, culture, education, as well as transport and communications.
- Both the Ganga and the Mekong are civilizational rivers, and the MGC initiative aims to facilitate closer contacts among the people inhabiting these two major river basins.
- The MGC is also indicative of the cultural and commercial linkages among the member countries of the MGC down the centuries.
|
- Defence cooperation:
- Defence partnership between the two countries have grown steadily since the signing of the Defence Protocol in 2000.
- Today, it covers exchange of intelligence, production and logistical support for Vietnam’s defence requirements, development of naval facilities such as Nha Trang, defence dialogues, joint military exercises and supply of warships and cruise missiles.
- India and Vietnam also recently agreed to the early finalization of the USD 500 million defence line of credit to Vietnam which would complement India’s ‘Make in India, Make for the world’ idea.
- Strategic cooperation:
- During the recent visit, an MoU was signed focused on mutual logistics support to enable the two countries to use each other’s military bases to repair and replenish supplies. This is the first agreement of its kind that Hanoi has entered into with any other country and will mainly benefit the Indian Navy as it ramps up its profile in the Indo-Pacific.
- Cultural cooperation:
- The two countries had signed a cultural agreement in 1976. Since then, many channels of cultural cooperation like the establishment of the Swami Vivekananda Indian Cultural Centre in Hanoi in 2016 have been established.
- Both countries have facilitated simplified visa regime to promote bilateral tourism. Around 1,69,000 Indians visited Vietnam and 31,000 Vietnamese visited India before the outbreak of the Covid-19 pandemic.
- Capacity building:
- Vietnam has been a large recipient of training programmes under Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) programme. Vietnam receives more than 200 training slots annually under ITEC.
- Indian Community:
- An estimated 5500 people from India, including some short-term visitors, constitute the Indian community in Vietnam. A majority of them are based in and around Ho Chi Minh City.
CHALLENGES TO STRONGER COOPERATION:
- China’s trade relations:
- China is the largest trading partner for both India and Vietnam. This trade dependency on China as well as its military superiority has led to an approach of cautious engagement between India and Vietnam.
- Trade deficit:
- Thought India’s trade deficit with Vietnam reduced from USD 2.22 billion during FY 2019-2020 to USD 1.12 billion in FY 2020-21, it is still a significant amount.
- Limited connectivity:
- India has proposed extending the India–Myanmar–Thailand Trilateral Highway (IMT highway) to Cambodia, Laos and Vietnam. However, the IMT highway was expected to be finished in 2016 but has not due to bureaucratic and procedural issues on the Indian side.
CONCLUSION:
The furtherance of India’s Act East Policy, maritime multilateralism, maritime security outreach, blue economy and the building of stronger networks across the Indo-Pacific are some of the key elements which makes New Delhi and Hanoi natural partners. Above this, China factor has provided impetus to the solidification of ties. Now both countries must ensure that the ties poised to develop further in the coming years.
PRACTICE QUESTION:
Q. Convergences of interests between India and Vietnam has naturally found expression in their bilateral relations. Discuss?
