India's Arctic policy
2022 MAR 15
Preliminary >
Geography > Economic geography > Economic geography
Why in news?
- The Centre released India’s Arctic Policy, with the aim of enhancing the country’s cooperation with the resource-rich and rapidly transforming region.
More about the news:
- Titled ‘India and the Arctic: building a partnership for sustainable development’, the policy is built on six central pillars :
- Science and research, climate and environmental protection, economic and human development, transportation and connectivity, governance and international cooperation.
- It was unveiled by Ministry of Earth Sciences.
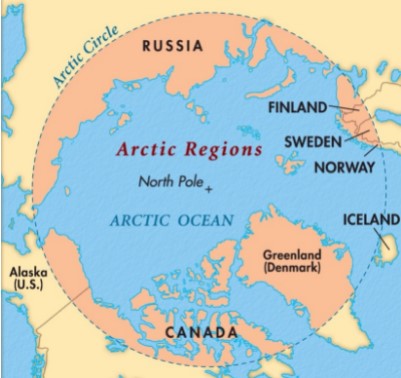
About Arctic region:
- It is commonly understood to refer to the region above the Arctic Circle, north of latitude 66° 34' N.
- The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Alaska (United States), Canada, Finland, Greenland (Denmark), Iceland, Norway, Russia, and Sweden.
- Climate: The Arctic's climate is characterized by cold winters and cool summers. The monthly average temperature in the Arctic is below 10 ° C throughout the year.
- Vegetation: Arctic vegetation is composed of plants such as dwarf shrubs, herbs, lichens, and mosses, which all grow relatively close to the ground, forming tundra. Trees rarely grow in the Arctic, but in its warmest parts, shrubs are common and can reach 2m in height.
- Human inhabitations: Only about 4 million people live in the Arctic worldwide. The economy mostly comprises of oil and gas extraction, fishing and tourism.
About India's Arctic policy:
- The policy, titled "India and the Arctic: building a partnership for sustainable development" lays down six pillars:
- Science and research activities
- Economic and human development cooperation
- Transportation and connectivity
- Governance and international cooperation
- National capacity building
- Its objectives are:
- Better understanding the scientific and climate-related linkages between the Arctic and the Indian monsoons.
- Harmonise polar research with the third pole (the Himalayas) and to advance the study and understanding of the Arctic within India.
- Exploration of opportunities for responsible exploration of natural resources and minerals
- Identifying opportunities for investment in Arctic infrastructure in areas such as offshore exploration/mining, ports, railways and airports.
- Developing fail-safe seed storage facilities in cryospheric regions
- Encouraging Indian participation in sustainable tourism in the Arctic.
- Sharing expertise in the management of indigenous and other communities with the Arctic states
- Cultural and educational exchanges between the indigenous communities of the glacial regions of the Himalayas and the Arctic.
- Participate in the environmental monitoring study to evaluate the predicted emissions of ships likely to traverse this route in future.
- Implementation
- In terms of implementation, the policy talks of an Action Plan and an implementation and review mechanism based on timelines, prioritisation of activities and allocation of resources.
- The implementation will involve all stakeholders including academia, the research community, business, and industry.
- Nodal Body:
- India has designated Goa-based National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research to lead scientific research and act as a nodal body to coordinate among various scientific bodies to promote domestic scientific research capacities in the Arctic.
The Arctic Council:
- It is the intergovernmental forum that addresses issues faced by the Arctic governments and the indigenous people of the Arctic.
- It comprises of eight countries with sovereignty over the lands within the Arctic Circle: Canada, Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia, Sweden, and the United States.
- Besides these members, there are several countries with observer status, which includes India and China.
- In 2011, the Council clarified its criteria for admission of observers, most notably including a requirement of applicants to "recognize Arctic States' sovereignty, sovereign rights and jurisdiction in the Arctic
PRACTICE QUESTION:
Consider the following statements:
1. Polar bears are largely found within the Arctic Circle only.
2. India is a permanent member of the Arctic council.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer
