Regulating Cryptocurrency
2022 DEC 2
Mains >
Science and Technology > Digital Technology > Innovation and New technologies
IN NEWS:
- FTX, one of the world’s biggest crypto exchanges, filed for bankruptcy protection.
- Brazil's Congress passed a bill that would regulate the use of cryptocurrency as a means of payment throughout the country, potentially providing a boost toward the adoption of digital assets in the South American nation.
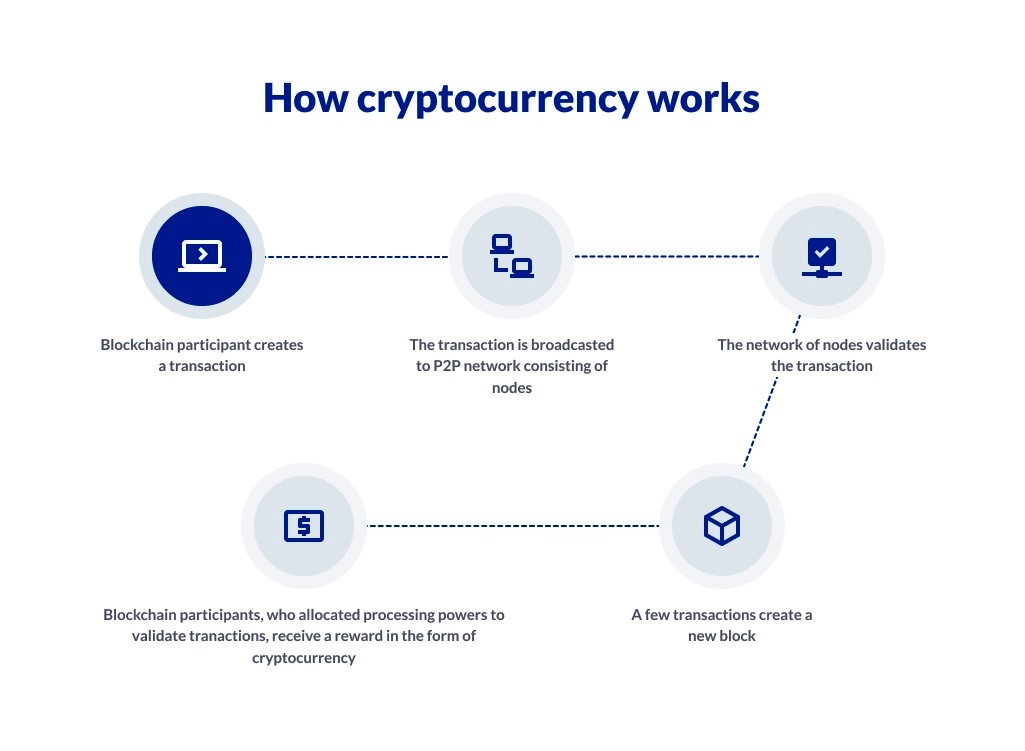
WHAT IS CRYPTOCURRENCY?
- A cryptocurrency is a form of digital or virtual currency based on a network that is distributed across a large number of computers.
- Many cryptocurrencies are decentralized networks based on blockchain technology.
- Bitcoin, first released as open-source software in 2009, is the first decentralized cryptocurrency. Other cryptocurrencies include Ethereum, Litecoin, Cardano, Polkadot, Stellar, Chainlink etc
-------------------
|
Blockchain:
- Blockchain is a system of recording information in a way that makes it difficult or impossible to change, hack, or cheat the system.
- A blockchain is essentially a digital ledger of transactions that is duplicated and distributed across the entire network of computer systems on the blockchain.
|
BENEFITS OF CRYPTO CURRENCY:
- User Autonomy:
- Digital currencies allow users more autonomy over their own money than fiat currencies do, at least in theory.
- The payment system is also peer-to-peer, meaning that users do not require any approval from any external source or authority to make transactions.
- Security:
- It is nearly impossible to counterfeit or double-spend.
- Decentralized:
- Users are able to control how they spend their money without dealing with an intermediary authority like a bank or government.
- Cost effective:
- Cryptocurrency users are not subject to the litany of traditional banking fees associated with fiat currencies like minimum balance fees, overdraft charges etc.
- The saving is more pronounced in international transactions.
- Privacy:
- Each cryptocurrency transaction is a unique exchange between two parties, which protects users from issues like identity theft.
- Accessibility:
- On a global scale, more people have access to the internet than they have to banks or other currency exchange systems.
- This opens the opportunity for underprivileged people to establish credit.
- Time saving:
- Transactions are instantaneous because the entire process is simple and requires very little time to process.
WHY DOES CRYPTOCURRENCY NEED TO BE BANNED?
- Undermines financial stability of the country:
- Cryptocurrencies are subjected to market fluctuations and the lack of a centralised authority makes it difficult to regulate them.
- As they lack a clear paper trail, tax evaders could use it as their tax havens in form of cryptocurrencies.
- Hence, they can easily undermine a country’s financial stability.
- Fuels illicit activities:
- Cryptocurrencies have been used as a mode of exchanging money for illegal activities, especially those on the dark web.
- Channel for money laundering:
- Given their decentralized nature and anonymity, cryptocurrencies are being used by some to launder their returns from illicit activities.
- Vulnerable to cyber threats:
- Although cryptocurrencies are very secure, exchanges are not that secure.
- Most exchanges store the wallet data of users to operate their user ID properly. This data can be stolen by hackers, giving them access to a lot of accounts.
- Impact on power consumption:
- Cryptocurrencies can have unfavorable consequences on India’s energy demand.
- Validating transactions in a distributed network involves high electricity consumption and requires high computation power.
- For eg: A study estimated that 19 households in USA can be powered for one day by the electricity consumed in a single transaction of bitcoin cryptocurrency.
|
Regulation in India:
- As of now, cryptocurrency does not have any legal status in India and are unregulated.
- In 2018:
- The RBI in its 2018 order had banned trading of all virtual currencies in India. The order restricted all entities regulated by the RBI not to deal with virtual currencies including maintaining accounts, registering, trading, settling, clearing, giving loans against virtual tokens, accepting them as collateral etc.
- In 2020:
- Supreme Court has struck down this ban on trading of virtual currencies (VC) in India.
- In 2021:
- The government has announced to introduce a bill; Cryptocurrency and Regulation of Official Digital Currency Bill, 2021, to create a sovereign digital currency and simultaneously ban all private cryptocurrencies.
- In Union Budget 2022-23:
- In the Union Budget 2022-23, the government categorically mentioned that the transfer of any virtual currency/cryptocurrency asset will be liable to 30 percent tax. Many cryptocurrency supporters see the declaration as the first step toward recognising cryptocurrencies as legitimate assets.
- The Union Budget 2022-2023 also proposed to introduce a digital currency in the coming financial year.
|
CONCLUSION:
- Cryptocurrencies are by definition borderless and require international collaboration to prevent regulatory arbitrage. Therefore, any legislation for regulation or for banning can be effective only after significant international collaboration on evaluation of the risks and benefits and the evolution of common taxonomy and standards.
- In this regard, government can look into some of the international best practices for regulating cryptocurrencies:
- In Russia, US and Japan, regulators have classified cryptocurrencies as either “intangible property” or legal payment methods to co-opt them in a bid to stop money laundering.
- The People’s Bank of China has done trial runs of its prototype cryptocurrency, taking it a step closer to being the first major central bank to issue digital money.
------------------- 
PRACTICE QUESTION:
Q. "Non-regulation of cryptocurrency is creating a big risk to national security and individual investors in India”. Discuss.

