Sports Industry in India
2022 AUG 18
Mains >
Economic Development > Indian Economy and issues > Miscellaneous
IN NEWS:
- FIFA, the governing body for world football, suspended the All India Football Federation for “undue interference by a third party”. This comes just days after India recorded a fabulous campaign at the Commonwealth Games 2022.
IMPORTANCE OF SPORTS FOR INDIA:
- Economic development:
- Sports is a multi-billion-dollar global industry propelled by enormous consumer demand. Encouraging sports can lead to the overall development of many allied sectors.
- Eg: Strengthening sports goods industry will boost India’s MSMEs, while encouraging sports medicine can promote research and development in better therapeutics for common man.

- Revenue generation:
- Sport can be a major contributor to the economy. For eg: Sports generates around USD 50 billion each year and accounts for 2-3% of Australia’s GDP. Fourteen million Australians participate in sport annually and 220,000 are employed across the sector.
- Employment generation:
- Sports offers careers as a sportsperson, coach, physical therapist, nutritionist, marketing, journalist, referee and sports lawyer, among others. There are professional courses and dedicated educational institutions to serve the individuals aspiring to make a career in the sports industry.
- Eg: In 2018, approximately 4.3 L people were employed in the sports industry of the UK.
- Infrastructure creation:
- Sports aids in the creation of infrastructure which benefit common masses. For instance, the 1982 Delhi Asiad facilitated the creation of first national TV service and introduced colour TV to India. New flyovers were added and roads were widened and 12,000 new phone lines and 150km of telephone cables were added to the city’s infrastructure.
- Aids in national integration:
- International events like the Olympics and the Cricket World Cup serve as a point around which to rally and show national pride and unity. This helps in developing a feeling of patriotism and unity that can counter regional factionalism and separatist forces.
- Social benefits:
- Channelize energy of youth positively: Sports help prevent youth from dropping out of school and counter threats like drug abuse and radicalization. This is why the sports events and infrastructure are given priority in areas like Jammu and Punjab.
- Overcome social barriers: Sports encourages interactions which helps to develop a culturally diverse community where individuals are not locked out from opportunities due to caste/ethnic/linguistic differences.
- Women empowerment: Some researches have found that involvement in sports seems to help women in breaking down barriers at workplace. Eg: many women in top executive positions have played sports at some level.
- Individual benefits:
- Playing sports helps develop life skills which helps to produce more balanced and successful adults. Sports help in elevating qualities like discipline, determination, sportsmanship teamwork and a passion for fitness in the psyche of an individual.
- Political significance:
- Sports is often utilized by countries as an arena to demonstrate their political aspirations to the world.
- Eg: 1964 Tokyo Olympics, 1988 Seoul Olympics and the 2008 Beijing Olympics propelled Japan, South Korea and China onto the global stage.
- Global Prestige:
- The medals and trophies earned by players at globally recognized sporting events bring glory and honour to the country.
EFFORTS TO PROMOTE SPORTS IN INDIA:
‘Sports’ being a state subject, the responsibility for development of sports rests with the State/Union Territory Governments. Central Government supplements their efforts in this regard.
Sports Authority of India is the premier sports body that is in charge of implementing the sports schemes to promote sports culture in India. The Ministry of Youth Affairs & Sports has formulated the following schemes to promote sports in the country, including in rural, tribal and backward areas:
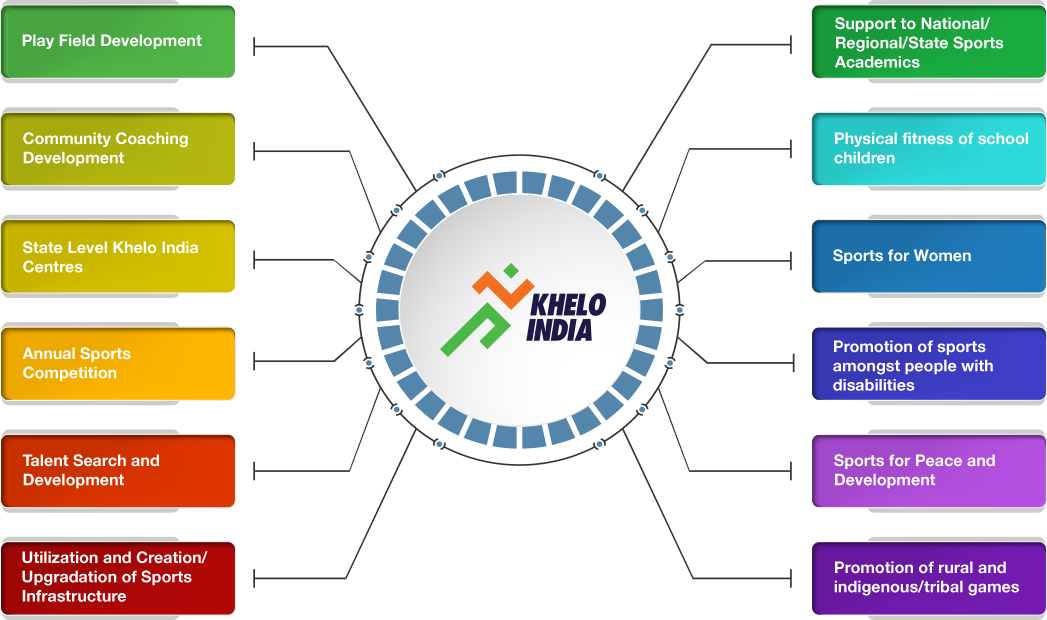
- Khelo India Scheme:
- In 2016, the government combined three existing schemes: the Rajiv Gandhi Khel Abhiyan, the Urban Sports Infrastructure Scheme and the National Sports Talent Search System—into the Khelo India scheme.
- India is divided into 5 zones namely North, East, West, South and North-East Zones to carry out talent identification.
- Talent search is started at grassroots level in two categories: Sports potential talent identification & Proven talent identification.
- Khelo India Athletes identified and selected under the scheme are provided annual financial assistance of Rs. 6.28 lakh per athlete.
- Target Olympic Podium Scheme:
- TOPS provides assistance to India’s top athletes. Under the Scheme, the Department of Sports shall identify athletes who are potential medal winners in 2020/2024 Olympics.
- Assistance to National Sports Federations
- Special Awards to Winners in International sports events and their Coaches
- National Sports Awards, Pension to Meritorious Sports Persons
- Pandit Deendayal Upadhyay National Sports Welfare Fund
- National Sports Development Fund
- Running Sports Training Centres
- Other efforts:
- FIT INDIA Movement to make fitness an integral part of our daily lives.
- Promotion of sports in the country is recognized as a CSR activity.
CHALLENGES IN MAKING SPORTS AS A CAREER:
- Lack of sporting culture:
- In India, sports is primarily viewed as a hobby, making it difficult for youth to pursue sports as a profession.
- Inadequate sports Infrastructure:
- At the grassroot level, sports infrastructure is rudimentary. Even at the top level, availability to world class sports equipments, training facilities, physio and nutrition is a major challenge.
- Eg: In 2019, Saina Nehwal refused to play at the Senior National Badminton Championship citing a poor playing surface at the venue in Guwahati.
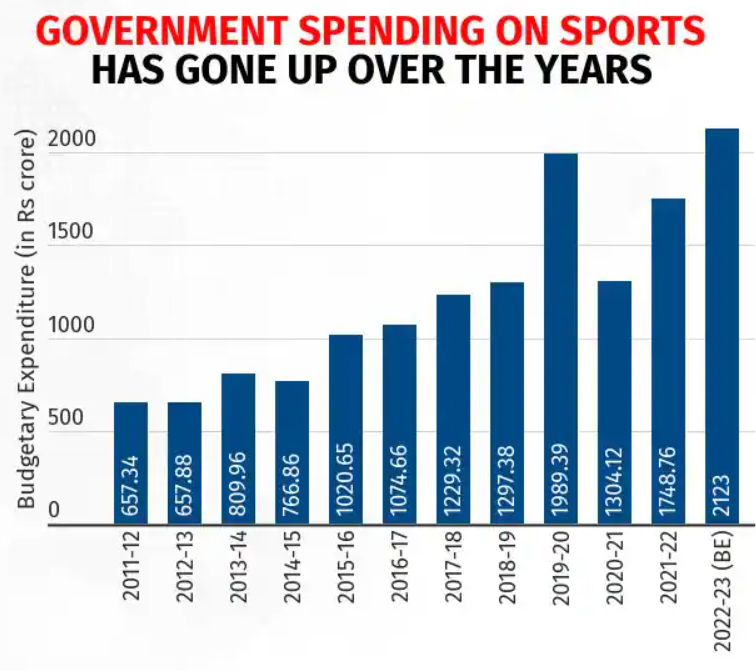
- Nominal government spending:
- The total allocation for sports in the Union budget 2022-23 stood at Rs 3062.60 cr, while China spends around 200 times more.
- Limited private investment:
- Corporate spending on promoting sports in India has been largely negligible when compared to government funding.
- Focus on a few sports:
- Most of the media attention and funds for promotion of sports goes either just to cricket or the more coveted formats like leagues, benefiting very few
- Issues in sports governance:
- Various sports governing bodies in India are accused of nepotism, fiefdom, unaccountability, political interference and financial irregularities. Eg: The All India Football Federation has been recently suspended by FIFA due to “third-party interference”.
- In some cases, there are multiple governing body, leading to governance paralysis. Eg: The tussle between Hockey India and Indian Hockey federation in early 2010s.
- Influence of illicit activities:
- Indian sporting arena has often been a victim of match fixing and money laundering. To add to this is the issue of using Performance Enhancing Drugs.
- Duplications in policy:
- Due to lack of coordination among the egencies, there are instances of duplication in policy measures.
- Eg: Both the Samagra Shiksha Abhiyaan and Fit India Movement are called upon to provide sports equipment to government schools and ensure maintenance.
- Lack of top class international sporting events
- Top athletes like Neeraj Chopra have suggested the need for regular top-class international meets in the country to generate interest and exposure for Indian athletes.
WAY FORWARD:
As per private researches, the sports sector in India as an industry is likely to go up five times to reach a value of USD 100 billion by 2027 from USD 27 billion in 2020. To tap into this potential and revive the sports culture, the government should revisit the sporting framework of India.
- Recognizing Sports as an Industry
- In a fast-growing economy like India, there is a tremendous potential for the sports sector to develop and achieve the status of an industry.
- Promoting Industry-based Sports Education Programmes
- Such as sport management programmes, sports medicine, sports nutrition, sports tourism and affiliated sectors.
- Assistance for R&D in Sports:
- The government must invest in promoting technological advances like sports analytics, sports medicine and development of affordable sports equipments.
- Provide Land and Invest in Sports Infrastructure through PPP Model
- Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model works best for building sports infrastructure. Also, a long-term land lease will help to get adequate land to build such facilities.
- Tap into emerging sports like eSports:
- eSports is a rapidly expanding industry that has drawn viewers and investments alike. If proper attention and support are given, India, with its young demography and strong IT sector, stands to gain from this sector.
PRACTICE QUESTION:
Q. Sports as an Industry is often overlooked in India. Discuss the potential of Sports in promoting economic development in India?


