10 years of BRI
2023 OCT 24
Mains >
International relations > Agreements > India-China
WHY IN NEWS
The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), led by Chinese President Xi Jinping, marked its 10th anniversary.
ABOUT BELT AND ROAD INITIATIVE
The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) is a global infrastructure development strategy launched by China in 2013. It aims to invest in over 150 countries and international organizations, creating road, rail, and sea routes for trade and connectivity. The initiative, often referred to as “One Belt One Road” (OBOR), is a key part of China’s foreign policy and has been compared to the American Marshall Plan.
OBJECTIVE OF BRI:
The BRI is seen as a way for China to transition to a global power and reshape the global economic order. It further aims to enhance global connectivity through infrastructure development and economic cooperation.
BRI includes various infrastructure projects like ports, railways, roads, and power stations. It is set to be completed by 2049, coinciding with the centennial of the People’s Republic of China. The initiative includes two principal components: the Silk Road Economic Belt and the Maritime Silk Road.
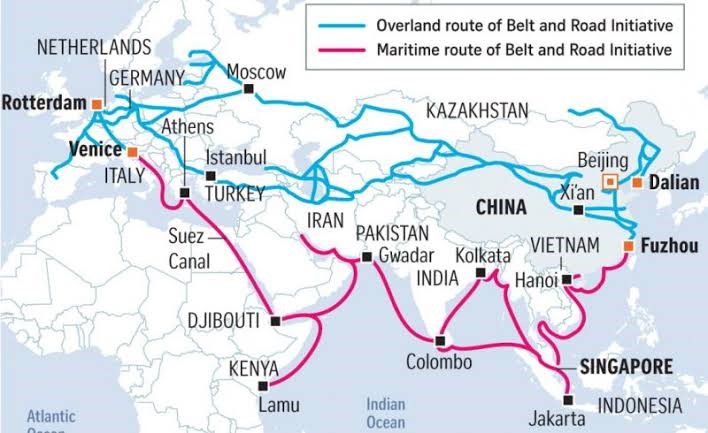
Geographic Corridors for BRI Development:
- China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC)
- New Eurasian Land Bridge Economic Corridor
- China-Indochina Peninsula Economic Corridor
- China-Mongolia-Russia Economic Corridor
- China-Central Asia-West Asia Economic Corridor
- China-Myanmar Economic Corridor (Initially, BRI involved the BCIM Economic Corridor, but India’s opposition to the CPEC led to its withdrawal from BRI and later BCIM was replaced by the China-Myanmar Economic Corridor).
BENEFITS OF BRI FOR CHINA AND OTHER COUNTRIES:
- Enhanced trade and economic influence: BRI expands China’s trade networks and bolsters its role in global economic affairs. Countries participating in BRI have gained preferential treatment and policy benefits.
- Outlet for excess capacity: BRI projects provide markets for Chinese industries, particularly in construction.
- Geopolitical and strategic influence: BRI increases China’s influence in participating countries and on the world stage.
- Currency internationalization: Promotes the use of the Chinese yuan (RMB) in international trade and finance.
- Energy security: BRI projects secure access to crucial energy resources for China.
- Technological innovation and knowledge sharing: BRI facilitates technology transfer and knowledge exchange between China and its partners.
CONCERNS RELATED TO THE BELT AND ROAD INITIATIVE (BRI):
- Sovereignty concern: India and other countries express sovereignty concerns over BRI projects like the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC).
- Strategic concern: India is worried about the strategic implications of BRI, including the impact on its maritime capabilities and regional influence.
- Lack of Transparency: Concerns have arisen due to the lack of transparency in BRI projects, particularly related to debt and loan conditions. BRI infrastructure project has encountered major implementation problems, such as corruption scandals, labour violations, environmental hazards, and public protests.
- Project Monopoly concern: Chinese state-owned enterprises dominate BRI investments, limiting competition and opportunities for other companies.
- Economic Viability : The lack of competition and high interest rates on loans have raised concerns about corruption and economic viability.
- Delays in Project: Some BRI projects face delays and challenges, leading to questions about the feasibility and impact of China’s ambitious strategy.
- Debt Trap: China is criticized for practising “debt-trap diplomacy,” where it lends money to countries like Sri Lanka and Zambia, who struggle to repay, leading to China acquiring strategic assets or political concessions.
- Multilateral Governance: Unlike initiatives like the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB), the BRI lacks a centralized governing structure, making it difficult to address issues collectively.
- Political Tensions: Geopolitical rivalries and disputes have affected BRI project implementation, potentially undermining progress.
- Environmental Concerns: BRI infrastructure projects have faced criticism for their environmental and social impacts, requiring sustainable development.
- Geostrategic Concerns: BRI projects will enhance China’s stature and undermine India’s influence over smaller South Asian countries and Indian Ocean littoral states.
ALTERNATIVES
- B3W Initiative: Led by G7 countries, it aims to address the infrastructure deficit in developing and lower-income countries. A repackaged version of B3W called ‘Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment’ by G7 has also been initiated to fund infrastructure projects in developing nations. India supports it.
- Blue Dot Network (BDN): A multi-stakeholder initiative by the US, Japan, and Australia to promote high-quality standards for global infrastructure development.
- India’s “IDEAS” plan: India’s counter to BRI, supported by Lines of Credit (LOCs) to countries in Asia, Africa, CIS, and Latin America. It includes initiatives like IMEC and INSTC.
- India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) initiative during the recent G20 summit.
- International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC) for connecting India to the Middle East and Russia.
- Global Gateway: Launched by the European Union to compete with BRI, focusing on various sectors, including climate change, digitalization, health, and education.
CONCLUSION
China, in order to go ahead and protect its own interests, has put in place a network of investments which has led to several low- and middle-income countries in severe debt hence the global initiatives have provided a counter block for monopoly and taken steps to focus on more inclusive and sustainable development.
PRACTICE QUESTION
The China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) is viewed as a cardinal subset of China’s larger ‘One Belt One Road’ initiative. Give a brief description of CPEC and enumerate the reasons why India has distanced itself from the same. (UPSC 2018)
