SAGAR (SECURITY AND GROWTH FOR ALL IN THE REGION)
2021 FEB 4
Mains >
International relations > India Foreign Policy > Maritime policy
WHY IN NEWS:
- Government of India is providing assistance to friendly foreign countries to overcome natural calamities and COVID-19 pandemic under the ‘Mission Sagar’, which is aligned with the India’s policy of ‘Security and Growth for All in the Region’ (SAGAR) for IOR islands.
BACKGROUND
- The strategic importance of Indian Ocean Region (IOR) is ever increasing to the world order in general and Indian sub-continent in particular.
- A secure IOR is key to ensuring security of India’s national interests.
- In 2015, India started SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region) strategy, making it the cornerstone of his engagement with the Indian Ocean rim and islands.
ABOUT THE ‘SAGAR’ STRATEGY
- Safeguard land and maritime territories and interests:
- Enhancing capacities to safeguard land and maritime territories and interests is major focus under SAGAR initiative.
- India has held multilateral naval exercises called Milan in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands with 16 other countries and in the Rim of the Pacific Exercise (RIMPAC).
- The success of maritime cooperative action against piracy in the Gulf of Aden is an example of the benefits of a cooperative approach which resulted in a dramatic decline in piracy incidents in the region.
- Expanding military strength:
- India has overseas military base in Duqm port (Oman); and coastal surveillance radar in Mauritius and Seychelles.
- Deepening economic and security cooperation:
- India engage with IOR littoral states in the areas of marine bio-technology, exploration and sustainable exploitation of ocean mineral resources, sustainable fishing practices, and harnessing of ocean energy.
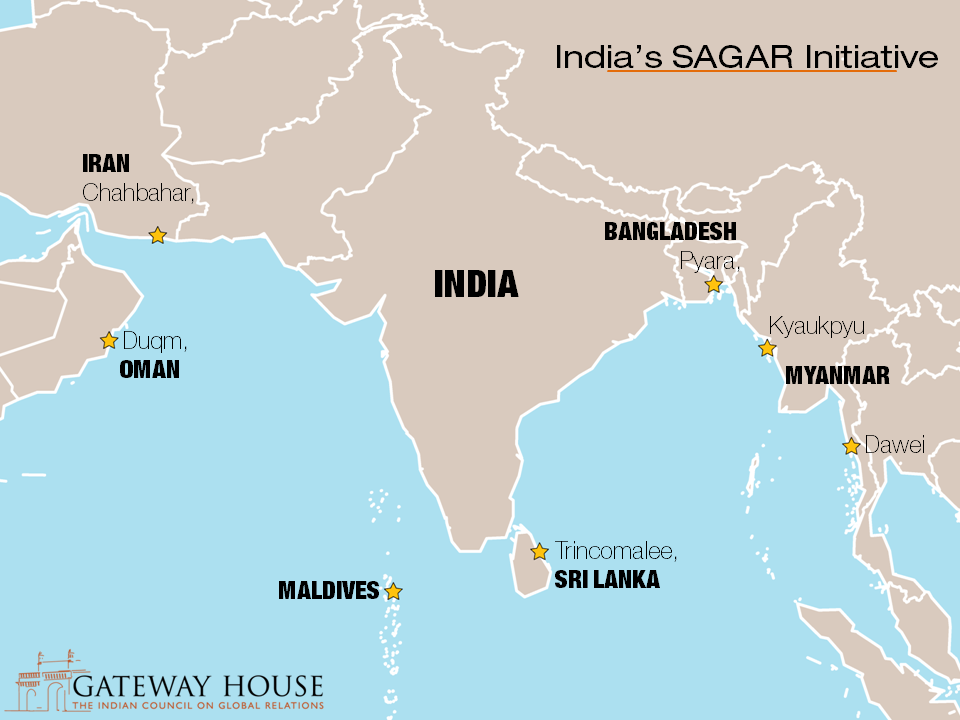
- India is committed to extending port connectivity among the littoral states of the Indian Ocean and beyond.
- Example: construction of Sittwe port
- Disaster management:
- Promoting collective action to deal with natural disasters is a goal under SAGAR.
- India is proactive in providing assistance to littoral islands during disaster.
- For example: India’s support to Madagascar which was ravaged by the Cyclone Ava.
- India provided 1,000 tonnes of fresh water to Male to help Maldives which is suffering from an acute drinking water crisis.
- Working towards sustainable regional development through enhanced collaboration:
- There is a renewed focus on strengthening marine research, developing eco-friendly marine industrial technologies, promoting sustainable fisheries and ensuring the protection of the maritime environment.
- 14 Coastal Economic Zones being developed under Sagarmala.
- Engaging with countries:
- Engaging with countries beyond our shores with the aim of building greater trust and promoting respect for maritime rules, norms and peaceful resolution of disputes is one of the goals under SAGAR.
- India is working on connectivity and infrastructure projects:
- For example: Kaladan transport project in Myanmar, Trilateral Highway between India-Myanmar-Thailand, Chabahar port project in Iran, Trincomalee Port in Sri Lanka etc.
NEED FOR ‘SAGAR’ STRATEGY
- Leveraging blue economy:
- Blue economy presents India with an unprecedented opportunity to meet its national socio-economic objectives as well as strengthening connectivity with neighbors.
- Increasing prominence of oceans:
- Oceans provide transportation for 80% of global trade.
- The seabed currently provides 32% of the global supply of hydrocarbons, with exploration expanding.
- The sea also offers vast potential for renewable blue energy production from wind, wave, tidal, thermal and biomass sources.
- New technologies are opening frontiers of marine resource development from bio-prospecting to mining of seabed mineral resources (poly-metallic nodules).
- Tackling regional issues:
- SAGAR helps to fulfill the need to strengthen efforts to provide humanitarian assistance in wake of natural disasters and counter non-state actors engaged in piracy and terrorism.
- Checking Chinese influence:
- China through its maritime silk route has been increasing its influence in Indian ocean region (IOR).
- Moreover, Chinese investments in India's neighboring countries are of dual nature i.e commercial with military underpinnings. The string of pearls has caused strategic concerns for India.
- In this context, SAGAR vision assumes much importance in countering such issues.
- To expand our strategic partnerships:
- SAGAR provides a mechanism for India to expand strategic partnerships with other IOR littorals in Asia and Africa.
- Aligned with India’s other foreign policies:
- The key relevance of SAGAR emerges when seen in conjunction with India’s other policies impacting the maritime domain like Act East Policy, Project Sagarmala, Project Mausam etc.
- Reinforces India’s role as ‘net security provider’ of IOR:
- SAGAR symbolises India’s maritime resurgence, as maritime issues are now centre of India’s foreign policy.
- With effective implementation of SAGAR policies, India can act as an enabler to create a positive environment in the IOR.
CHALLENGES TO ‘SAGAR’:
- Chinese assertiveness:
- Debt diplomacy- Sri Lanka was forced to lease Hambantota port to China for 99 years, as they failed to repay the loan
- String of pearls strategy
- Weaponization of maritime supply chain – Chinese commercial projects under BRI has military applications too
- Setting up of overseas base. Ex: Great coco island, Myanmar
- Poses a risk for overexploitation of marine resources:
- The ‘Global Commons’ approach to using marine resources, especially in areas beyond national jurisdiction, with no oversight >> poses risk of over-exploitation
- For example IUCN report suggests deep sea mining in IOR threatens unique species in remote locations
- Unresolved sovereignty issues:
- For example dispute over Chagos Archipelago by UK and Mauritius
- Ecological issues:
- Marine pollution. For ex: recent oils spills in coast of Mauritius
- Diminishing fishing resource in IOR. FAO reported that 74% of fish in South West Indian ocean had been fished to their limits
- Security concerns:
- Traditional security challenges such as militarization, maritime muscle flexing etc.
- Non-traditional threats such as piracy, drug trafficking, terrorism etc.
WAY FORWARD
- Formulating a governance framework
- A regional legally-binding instrument concerning marine genetic resource governance including issues of access to genetic resources and benefit sharing (ABS) is to be concluded within the framework of the UN Convention on the Law of the Seas (UNCLOS).
- Promoting sustainable development in IOR:
- There is a need to identify areas for designating as special ecologically and biologically sensitive areas to ensure such areas receive additional protection and sustainable management provisions.
- Focusing on regional organizations:
- India must focus on the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA), Indian Ocean Commission (IOC), Indian Ocean Naval Symposium etc. to promote sustainable growth and balanced development in the region.
- Focus on Project Sagarmala:
- There is a need to make a tangible impact through Project Sagarmala, with a focus on port development, connectivity, port-led industrialisation, and coastal community development, in a timely and effective manner.
- Increased role of the Coast Guard Agencies:
- Role of Coast Guard Agencies in all the Indian Ocean littorals becomes critical
- Therefore, SAGAR vision should now be expanded to include the coast guard agencies of the IOR littorals countries.
- Ensuring overall development:
- SAGAR vision should not only tap the potential of oceans and marine areas for economic development of member states but also consider focusing on contribution to achieving the Sustainable Development Goals.
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. SAGAR strategy helps India to tackle maritime security challenges at the macro level in the Indian Ocean region? Critically analyze
